Redox Homeostasis and Bio(in)organic Chemistry of Reactive Sulfur Species: Probes
Team Composition
Permanent Staff
E. Galardon, CR, HDR
S. Lajnef, IE
D. Over, MCU HC
F. Peyrot, MCU, HDR
M. Poinsot, IE
PhD Students
We are interested in the development of new probes, with an emphasis on the design of fluorescent and optical probes for hydrogen sulfide, and on the development of redox-sensitive EPR probes for the monitoring of redox homeostasis deregulation.
Redox-sensitive EPR probes
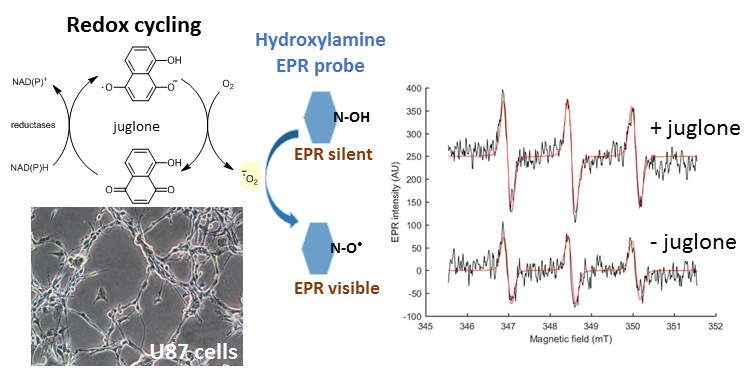
EPR spectroscopy in association with molecular probes has been successfully applied to monitor the redox status of tumors or to assess various pathological conditions in rodent models. However, commercially available molecular probes are extremely limited in number, and they display poor biostability and specificity that makes the interpretation of observations difficult.
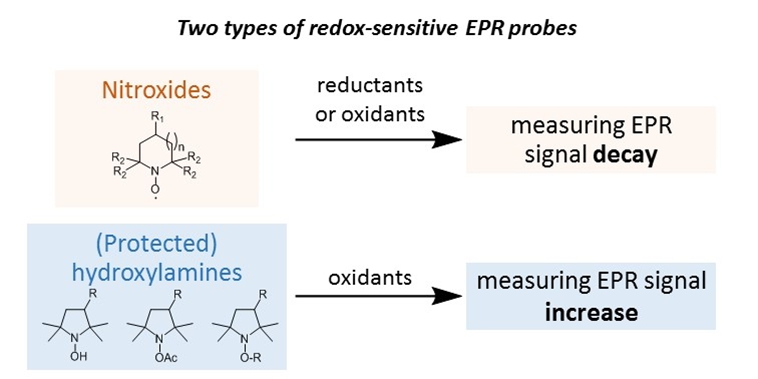
In recent years, we started addressing this problem by developing new redox-sensitive probes derived from tetraethyl-substituted nitroxides or (protected) hydroxylamines. Formulation of these lipophilic probes using nanoemulsions is required for in vivo applications (collaboration with Dr C. Roques, Unité de Technologies Chimiques et Biologiques pour la Santé, Université de Paris, and with Pr M. Mojović, Faculty of Physical Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Serbia).
Fluorescent & optical probes for H2S
Latest publications (full list here)
Unexpected rapid aerobic transformation of 2,2,6,6-tetraethyl-4-oxo(piperidin-1-yloxyl) radical… Babić N, Orio M, Peyrot F. Free Radic. Biol. Med., (2020)
New synthetic route to 2,2,6,6-tetraethylpiperidin-4-one: A key-intermediate…
Babić N., Peyrot F. Tetrahedron Lett. (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2019.151207
Redox Homeostasis and Bio(in)organic Chemistry of Reactive Sulfur Species: Probes
We are interested in the development of new probes, with an emphasis on the design of fluorescent and optical probes for hydrogen sulfide, and on the development of redox-sensitive EPR probes for the monitoring of redox homeostasis deregulation.
Redox-sensitive EPR probes
In recent years, we started addressing this problem by developing new redox-sensitive probes derived from tetraethyl-substituted nitroxides or (protected) hydroxylamines. Formulation of these lipophilic probes using nanoemulsions is required for in vivo applications (collaboration with Dr C. Roques, Unité de Technologies Chimiques et Biologiques pour la Santé, Université de Paris, and with Pr M. Mojović, Faculty of Physical Chemistry, University of Belgrade, Serbia).


Fluorescent & optical probes for H2S
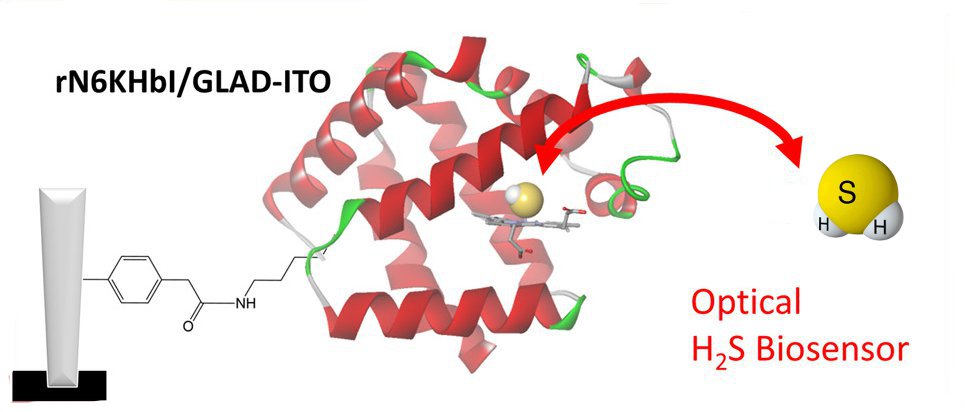
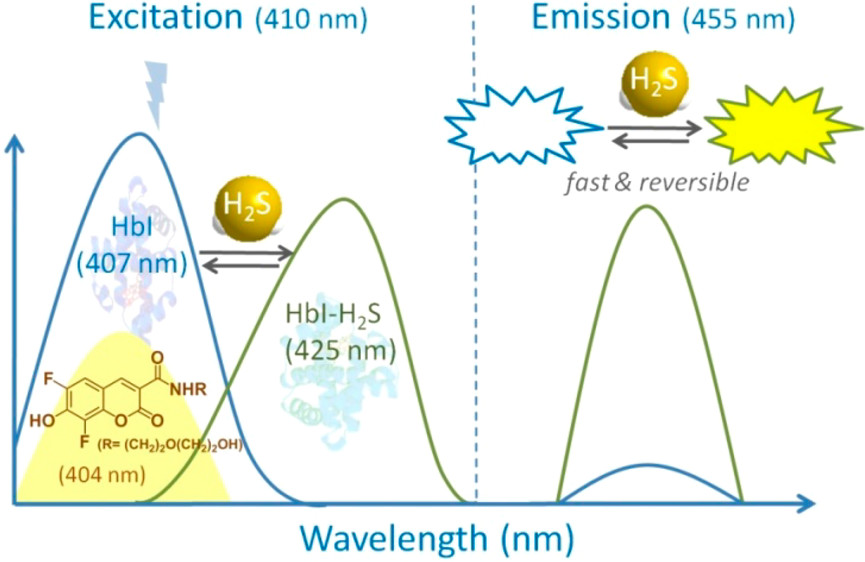
We used recombinant Hemoglobin I Hb-I from the clam Lucina pectinata, a protein which rapidly, selectively and reversibly bind H2S with high affinity, to propose a fluorescent system in solutionand an optical biosensor resulting from the grafting of Hb-I on mesoporous transparent conductive electrodes. Both system can reversibly detect H2S at low concentration (approx. 1 µM) in biological fluids like human plasma (In collaboration with Dr V. Balland, Laboratoire d’Electrochimie Moléculaire, Université de Paris)


